Lean methodology has stood the test of time, offering businesses a framework to enhance efficiency and eliminate waste. Despite its roots dating back decades, with seminal works like Lean Thinking by Womack & Jones (1996) and The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Lean by Flinchbaugh & Carlino (2006), the principles of Lean continue to be highly relevant.
This guide will revisit and expand upon these timeless strategies, adapting them to the contemporary market environment.
Defining Value: Starting with the Customer
Every Lean journey commences with a fundamental question: What does the customer value? Understanding and defining customer value is crucial. It’s not just about identifying what customers are willing to pay for, but also recognizing what they do not value.
Clarity here sets the direction for all subsequent actions and aligns the entire process towards delivering that value efficiently.
Streamlining Processes by Eliminating Waste
Contrary to popular belief, Lean isn’t solely about cutting waste—it’s a comprehensive approach to enhancing overall value. Once customer value is clearly defined, the next step is to scrutinize every process step, identifying and eliminating anything that doesn’t add value.
This involves mapping out the value stream and actively removing the seven classic forms of waste: defects, overproduction, waiting, non-utilized talent, transportation, inventory, and extra processing.
Ensuring Smooth Operations through Flow
Post-waste elimination, the focus shifts to optimizing the flow of operations. This means arranging process steps so they proceed smoothly and predictably towards delivering customer value.
It involves observing operations firsthand and understanding the interconnectedness of activities, which helps in minimizing delays and improving service delivery.
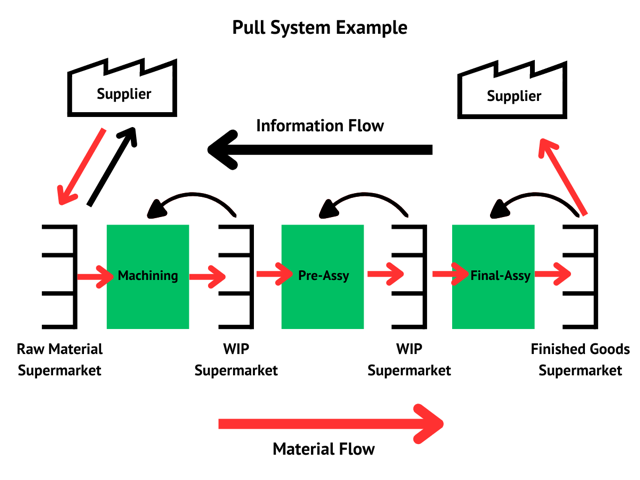
Responsive Production with Pull Systems
Implementing a pull system is a transformative step in Lean methodology. It shifts the production control to be driven by actual demand rather than forecasts.
This is facilitated by signals like Kanban, which ensure that resources are replenished just in time, based on customer or downstream demand, thereby reducing excess inventory and improving responsiveness.
Building a Lean Culture
Lean transformation extends beyond process changes—it necessitates a cultural shift within the organization. Effective communication plays a pivotal role in this regard, preventing misconceptions and resistance among employees.
Establishing a shared understanding of Lean terms and visual cues, and fostering a learning environment focused on continuous problem-solving are essential for sustained success.
Driving Long-term Success through Sustainability
The ultimate goal of Lean is not just to implement changes but to sustain them and seek continuous improvement. This requires transparency, ongoing goal setting, and a relentless pursuit of perfection.
Organizations should regularly reflect on their Lean journey, celebrate achievements, and set new objectives to ensure long-term success.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, Lean principles offer a proven framework for organizations aiming to streamline operations and enhance customer value.
By revisiting and adapting these principles, businesses can stay agile and responsive to changing market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions about Lean Principles
How does defining customer value benefit a business?
Defining customer value allows a business to focus its efforts on what truly matters to its customers, ensuring resources are allocated effectively.
It helps in eliminating processes that do not add value, thus reducing waste and increasing efficiency. This alignment with customer expectations not only improves satisfaction but also drives loyalty and revenue.
Can you explain the seven types of waste in Lean?
The seven types of waste in Lean include defects, overproduction, waiting, non-utilized talent, transportation, inventory, and extra processing.
Each represents an inefficiency that costs time, resources, and money. By identifying and eliminating these wastes, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve quality.
What are the benefits of implementing a pull system in production?
A pull system in production controls the flow of resources by responding to actual demand rather than anticipated demand.
This helps reduce overproduction and excess inventory, minimizes storage costs, and enhances flexibility and responsiveness to market changes. It ensures that products are produced just in time, improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
How can an organization sustain Lean principles in the long term?
Sustaining Lean principles involves creating a culture of continuous improvement where every employee is engaged in identifying inefficiencies and suggesting improvements.
Regular training, clear communication, and visible leadership commitment are essential. Setting short and long-term goals, along with regular reviews of Lean initiatives, helps maintain focus and momentum toward achieving a Lean environment.
News By Month
Recent Posts
- Smart Electric Tugs: The Key to Efficiency, Safety, and Well-being in Transportation and Logistics
- The Financial and Safety Benefits of Hovmand Lifting Solutions: See Us at PACK EXPO
- 5 Ways Lean Manufacturing Principles Can Boost Your Bottom Line
- How Lean Manufacturing Practices Automate Workflows
- Expanding the Lean Philosophy Beyond Misconceptions - What Lean is NOT
- Optimizing Lean Principles for Today's Business Environment
- How Implementing Gravity Conveyors in Your Warehouse Can Improve Productivity
- The History and Infinite Applications of Aluminum Extrustion Profiles
- What are Flow Racks and How Can They Improve Your Manufacturing?
- The History and Applications of Unistrut
